In This Article
- Key Takeaways
- What Is a Venture Studio?
- How Does the Venture Studio Model Work?
- Venture Studio vs Traditional VC: Understanding the Key Differences
- Benefits of the Venture Studio Model
- Venture Studio Equity Structure and Compensation
- Types of Venture Studios
- Successful Venture Studio Examples
- Common Questions About Venture Studios
- Conclusion
- Key Takeaways
- What Is a Venture Studio?
- How Does the Venture Studio Model Work?
- Venture Studio vs Traditional VC: Understanding the Key Differences
- Benefits of the Venture Studio Model
- Venture Studio Equity Structure and Compensation
- Types of Venture Studios
- Successful Venture Studio Examples
- Common Questions About Venture Studios
- Conclusion
What Is a Venture Studio? Model, Equity Structure, Benefits & Examples
A venture studio is a systematic company-building organization that creates multiple startups from scratch by providing operational support, shared resources, and initial funding—functioning as a "startup factory" that achieves 30% higher success rates than traditional startups. Unlike venture capital firms that invest in existing companies, venture studios actively ideate, validate, and build new ventures internally while taking significant equity stakes (typically 30-60%) in exchange for their comprehensive involvement in the startup creation process.
Key Takeaways
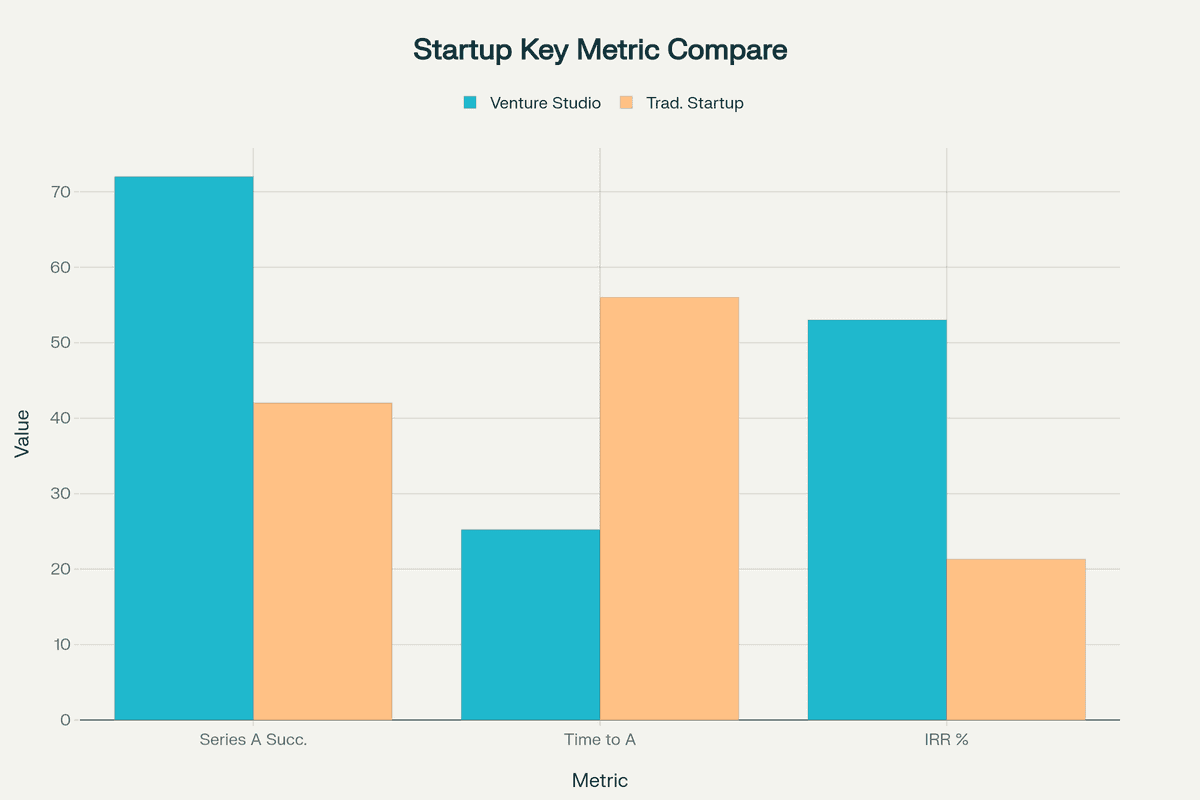
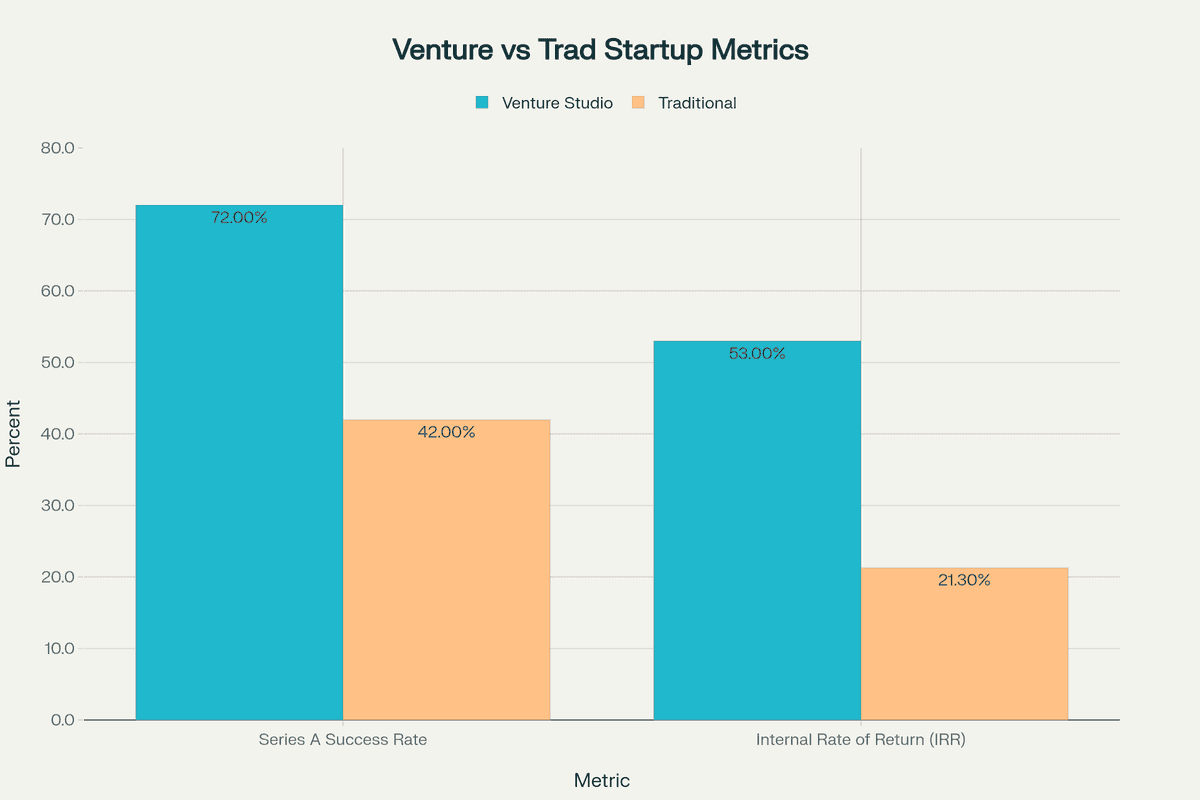
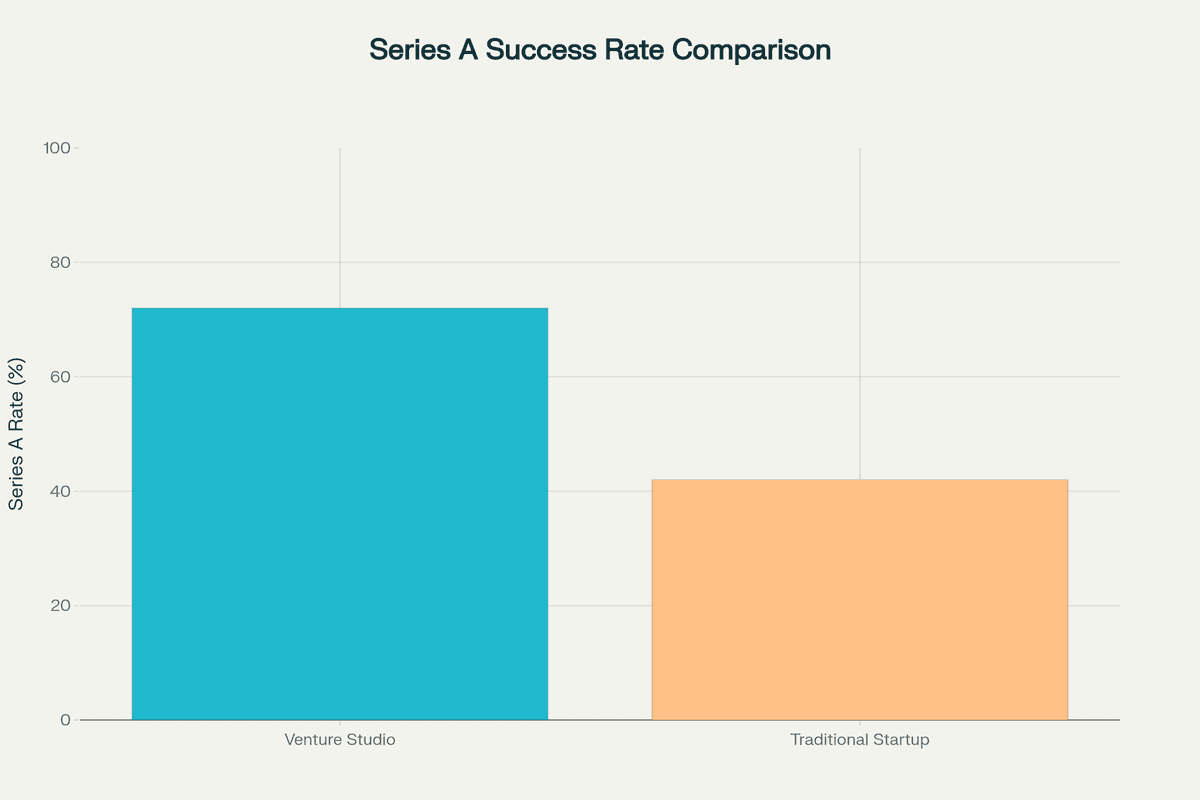
- Venture studios achieve 84% seed funding rates and 72% Series A success rates compared to 42% for traditional startups
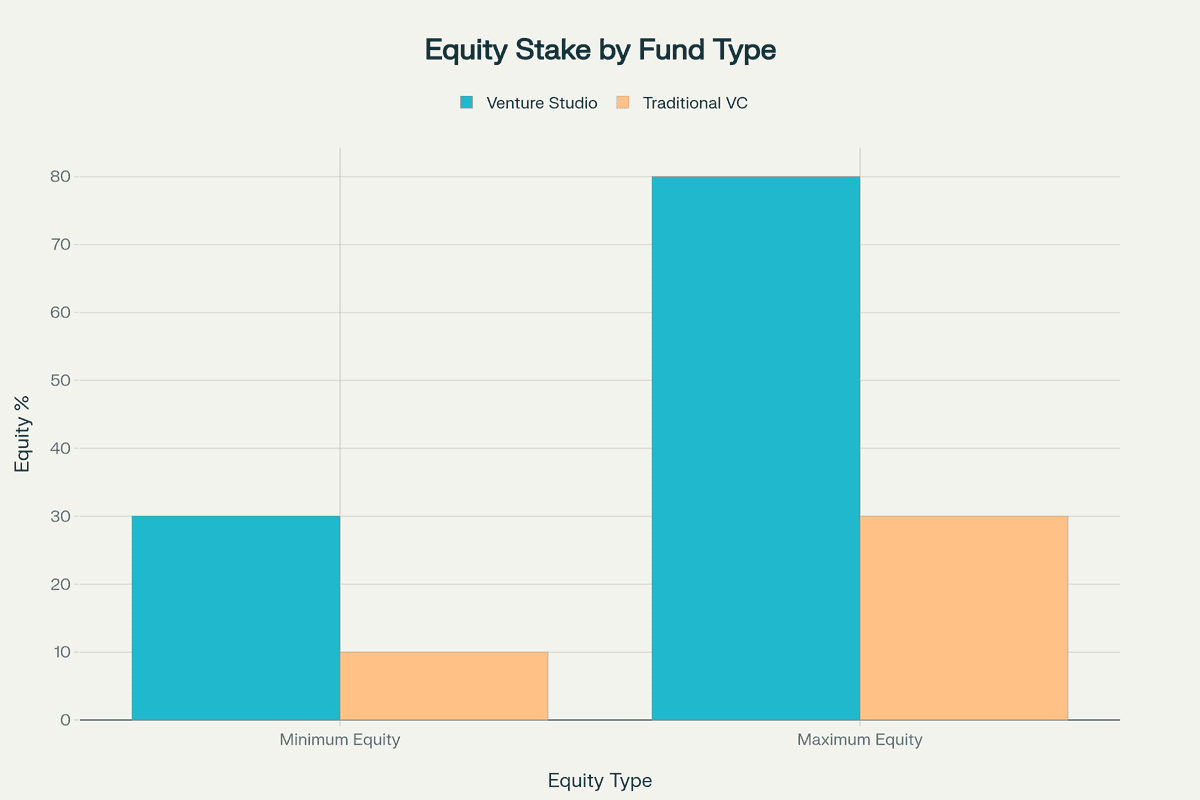
- Studios typically take 30-60% equity while providing complete operational support, funding, and shared resources
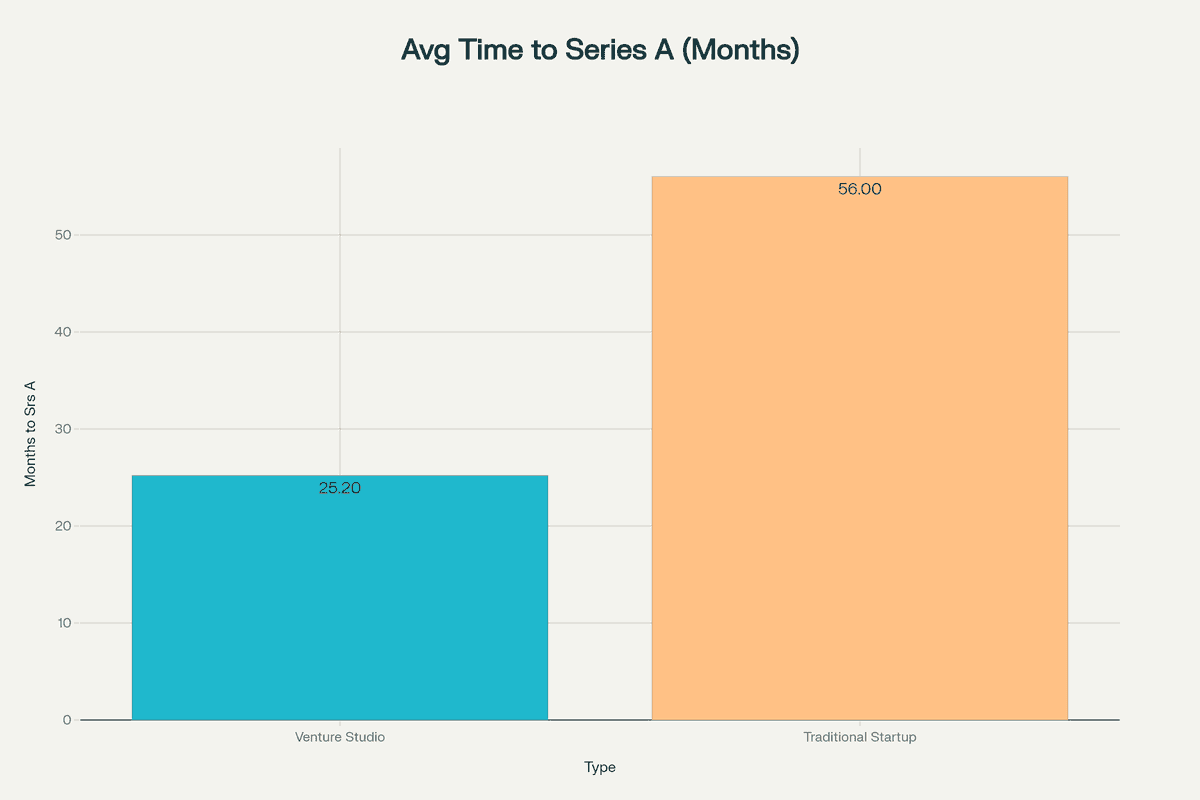
- The model reduces time to Series A by over 50% (25.2 months vs 56 months for traditional startups)
- Studios operate through systematic processes: ideation, validation, team formation, and scaling with proven playbooks
- Major successes include companies like Hims & Hers, Dollar Shave Club, and Overture (sold for $1.63B)
What Is a Venture Studio?
A venture studio, also known as a startup studio, venture builder, or startup factory, is a company that systematically creates new businesses by combining internal ideation, operational expertise, and capital under one organizational structure. The model operates on three fundamental principles that distinguish it from other startup support mechanisms.
First, venture studios engage in active company creation—they don't merely fund existing startups but generate ideas internally, validate market opportunities, and build companies from inception. Second, they provide systematic resource sharing through centralized services including product development, design, engineering, marketing, legal, and administrative support across their portfolio. Third, studios take higher equity ownership (30-60%) compared to traditional VCs (10-20%) to compensate for their extensive operational involvement and resource commitment.
The venture studio model represents a fundamental shift from traditional entrepreneurship. Where conventional startups rely on individual founders to navigate every aspect of company building, studios apply factory-like efficiency to startup creation. They maintain dedicated teams of designers, developers, marketers, and operators who work across multiple ventures simultaneously, dramatically reducing the time and cost of launching new companies.
Studios typically evaluate hundreds of ideas annually, subjecting each to rigorous validation processes before committing resources. This disciplined approach—killing approximately 85% of concepts early—ensures capital and talent concentrate on ventures with genuine market potential and scalability.
How Does the Venture Studio Model Work?
The venture studio model operates through a systematic four-stage process designed to minimize risk while maximizing the probability of startup success.
Stage 1: Ideation and Opportunity Identification
Studios begin by leveraging their domain expertise, market research, and industry networks to identify high-potential business opportunities. Ideas emerge from multiple sources: analysis of market gaps, problems encountered by studio founders in previous ventures, emerging technologies with commercial potential, and insights from industry partners. Studios typically aim for opportunities with addressable markets exceeding $1 billion.
Stage 2: Rigorous Validation
Once potential concepts are identified, studios employ data-driven validation methodologies including market research and competitive analysis, customer discovery through structured interviews, rapid prototyping and MVP development, landing page tests to gauge demand, and pre-sales or letters of intent from potential customers. This validation phase typically lasts 4-12 weeks, with clear metrics determining whether to proceed or terminate each concept.
Stage 3: Company Formation and Team Assembly
Validated concepts move into active company building. Studios assemble founding teams through three primary approaches: recruiting experienced Entrepreneurs-in-Residence (EIRs) to lead validated concepts, promoting high-performing internal studio employees to founder roles, or partnering with domain experts who bring specialized knowledge. The studio provides comprehensive infrastructure including legal entity formation, initial funding, office space and technology resources, and recruitment of key early employees.
Stage 4: Launch and Scale
With teams in place and initial products developed, studios support ventures through market launch and growth. This includes ongoing product development support, customer acquisition and go-to-market strategy, follow-on funding through studio funds or external investors, operational support in finance, HR, and administration, and strategic guidance through board participation.
Throughout this process, studios maintain active involvement, distinguishing them from passive investors. They function as co-founders, embedding their expertise into each venture's DNA while maintaining the flexibility to pivot or terminate underperforming concepts quickly.
Venture Studio vs Traditional VC: Understanding the Key Differences
While both venture studios and traditional VCs provide capital to startups, their approaches, involvement levels, and value propositions differ fundamentally.
Stage of Engagement: Traditional VCs typically invest in existing companies that have already validated their concepts and built initial teams. Venture studios create companies from scratch, often beginning with just an idea or market insight.
Operational Involvement: VCs provide strategic guidance, board oversight, and network connections but leave day-to-day operations to founders. Studios embed operational teams directly into ventures, providing hands-on support in product development, marketing, recruiting, and administration.
Risk Profile: Traditional VCs spread risk across large portfolios (often 50+ companies), expecting a few winners to generate returns. Studios concentrate resources on fewer ventures (typically 3-6 annually) but dramatically reduce execution risk through direct involvement.
Equity Stakes: VCs typically take 10-20% equity in exchange for capital. Studios command 30-60% equity, reflecting their role as co-founders who contribute ideas, teams, infrastructure, and funding.
Value Creation: Where VCs primarily add value through capital and strategic counsel, studios create value through systematic company building, shared resources, proven playbooks, and reduced time-to-market.
Success Metrics: The data reveals striking performance differences. Studio-backed ventures achieve an average IRR of 53% versus 21.3% for traditional startups. They reach key milestones faster, with 84% securing seed funding compared to 42% for conventional ventures.
This fundamental difference in approach explains why venture studios have emerged as a distinct asset class, attracting entrepreneurs who value operational support over maximum equity retention and investors seeking higher success rates with deeper portfolio engagement.
Benefits of the Venture Studio Model
For Entrepreneurs
Dramatically Reduced Risk: Studios provide salaries, benefits, and operational support from day one, eliminating the personal financial risk that typically accompanies entrepreneurship. Founders can focus on building without worrying about paying rent or healthcare.
Accelerated Time-to-Market: Access to pre-built infrastructure, experienced teams, and proven methodologies enables ventures to move from concept to market 50% faster than traditional startups. Studios eliminate the need to build basic operational capabilities from scratch.
Higher Success Probability: With 30% higher success rates than traditional startups, studio ventures benefit from systematic de-risking at every stage. The studio's experience helps avoid common pitfalls that doom many first-time ventures.
World-Class Resources: Entrepreneurs gain immediate access to senior designers, engineers, growth marketers, and operators who might otherwise be unaffordable or unavailable to early-stage ventures.
Validated Founder-Market Fit: Studios match entrepreneurs with opportunities aligned to their skills and experience, increasing the likelihood of success compared to founders pursuing ideas in unfamiliar domains.
For Investors
Systematic Deal Flow: Rather than sifting through thousands of pitches, investors access a curated pipeline of professionally-managed ventures that have passed rigorous validation.
Reduced Downside Risk: The studio model's systematic approach reduces complete failures. Even unsuccessful ventures typically achieve some value creation or generate learnings applicable to future ventures.
Operational Transparency: Unlike traditional VC investments where visibility is limited to board meetings and reports, studio investors maintain real-time insight into portfolio company operations.
Efficient Capital Deployment: Shared resources mean studios can validate and launch multiple ventures with less capital than would be required for the same number of independent startups.
Concentrated Expertise: Many studios focus on specific sectors, allowing investors to gain targeted exposure to industries where the studio has demonstrated competitive advantages.
Venture Studio Equity Structure and Compensation
The equity structure in venture studio startups reflects the studio's dual role as co-founder and investor, creating arrangements that differ significantly from traditional startup equity splits.
Typical Equity Distribution
While specific arrangements vary by studio and venture, common equity allocations include:
- Venture Studio: 30-60% for ideation, validation, resources, and initial capital
- Founding Team: 20-40% for the entrepreneurs leading the venture
- Employee Option Pool: 10-20% reserved for key hires
- External Investors: Remaining equity for subsequent funding rounds
This structure reflects the studio's contributions of intellectual property, validation work, operational support, and capital investment. The higher studio ownership percentage compensates for resources that would otherwise require significant founder investment or dilution through multiple funding rounds.
Vesting Arrangements
Studios typically implement sophisticated vesting structures that align long-term incentives:
Time-Based Vesting: Standard four-year vesting with one-year cliffs apply to founder and employee equity, ensuring commitment before shares vest.
Milestone-Based Components: Portions of equity may vest based on achieving specific targets such as product launch, revenue thresholds, or funding milestones.
Performance Accelerators: Acceleration clauses protect stakeholders in exit scenarios, ensuring fair treatment for value created.
Founder Compensation Models
Studios employ various compensation approaches to balance risk and reward:
-
Market Salary Plus Equity: Founders receive competitive salaries plus their equity stake, providing financial stability while building.
-
Below-Market Salary, Higher Equity: Some founders accept reduced cash compensation in exchange for larger ownership percentages.
-
Staged Compensation: Salaries increase as ventures hit predetermined milestones, conserving cash while rewarding progress.
-
Profit Sharing Models: Advanced studios implement carried interest or profit-sharing mechanisms that provide additional upside across the portfolio.
These structures aim to create sustainable building environments where founders can focus on value creation without personal financial distress while maintaining strong performance incentives.
Types of Venture Studios
The venture studio ecosystem has evolved to include several distinct models, each optimized for different markets, technologies, and stakeholder needs.
Industry-Focused Studios
These studios concentrate expertise and resources on specific sectors:
- Fintech Studios: Build financial technology ventures leveraging regulatory knowledge and banking relationships
- Healthcare Studios: Navigate complex medical regulations while developing digital health and medtech solutions
- Enterprise Studios: Create B2B SaaS companies with deep understanding of corporate buyer needs
- Climate Tech Studios: Focus on sustainability and environmental solutions requiring specialized technical knowledge
Technology-Platform Studios
These studios leverage core technical capabilities across multiple ventures:
- AI/ML Studios: Apply artificial intelligence to diverse industry problems
- Blockchain Studios: Build decentralized applications and Web3 infrastructure
- IoT Studios: Create connected device ecosystems with shared hardware expertise
Corporate Venture Studios
Established by large corporations to drive innovation beyond traditional R&D:
- Access parent company assets, customers, and distribution channels
- Focus on strategic areas aligned with corporate priorities
- Provide structured paths for acquisition or integration of successful ventures
- Balance startup agility with corporate resources and stability
Geographic Studios
Studios optimized for specific regions or markets:
- Emerging Market Studios: Adapt proven models for developing economies
- Regional Studios: Focus on local market opportunities and regulatory environments
- Cross-Border Studios: Build ventures designed for international expansion from inception
Each model offers distinct advantages, allowing entrepreneurs and investors to choose studios aligned with their specific goals, expertise, and market opportunities.
Successful Venture Studio Examples
Idealab - The Original Pioneer
Founded in 1996 by Bill Gross, Idealab created the venture studio model. With over 150 companies launched and 45+ successful exits, Idealab pioneered systematic startup creation. Notable successes include Overture Services (sold to Yahoo for $1.63 billion), which invented pay-per-click advertising, Picasa (acquired by Google), and CitySearch. Idealab's methodology of rapid prototyping and market testing established frameworks still used by studios today.
Rocket Internet - The Replication Machine
The Samwer brothers' Rocket Internet perfected the art of identifying successful business models and rapidly scaling them in new markets. With 200+ ventures and dozens of billion-dollar exits including Zalando, Delivery Hero, and HelloFresh, Rocket demonstrated that systematic execution could be as valuable as original innovation. Their playbook approach to company building influenced an entire generation of venture builders.
eFounders/Hexa - The SaaS Specialists
Starting as eFounders and rebranding to Hexa, this Paris-based studio has created over 30 B2B SaaS companies with combined valuations exceeding $5 billion. Successes include Front (customer communication platform), Aircall (cloud-based phone system), and Spendesk (spend management platform). Hexa's model of providing complete operational teams to entrepreneur-partners has proven particularly effective in the complex B2B software space.
Atomic - The Consumer Innovation Lab
Founded by serial entrepreneur Jack Abraham, Atomic has created multiple unicorns including Hims & Hers (NYSE: HIMS) and OpenStore. Atomic's approach emphasizes rapid iteration and data-driven decision making, with dedicated teams working on multiple concepts simultaneously until market validation confirms which to scale.
High Alpha - The B2B Factory
This Indianapolis-based studio combines venture building with a traditional VC fund, exclusively focused on B2B SaaS. Portfolio companies like Zylo (SaaS management), Lessonly (training software, acquired by Seismic), and Sigstr (email signature marketing, acquired by Terminus) demonstrate the power of deep vertical focus.
Science Inc. - The Exit Machine
Science Inc. has generated multiple billion-dollar exits including Dollar Shave Club (sold to Unilever for $1 billion), proving that studios can create ventures with massive exit potential. Their portfolio spans consumer brands, marketplaces, and software companies, showing the versatility of the studio model.
Common Questions About Venture Studios
How much equity do venture studios typically take in their startups?
Venture studios typically take 30-60% equity in their portfolio companies, significantly higher than the 10-20% traditional VCs take. This larger stake compensates for the studio's role as co-founder, providing not just capital but also the initial idea, validation, operational support, and shared resources throughout the company's development.
What's the difference between a venture studio and an accelerator?
While accelerators provide temporary support (usually 3-6 months) to existing startups in exchange for 5-10% equity, venture studios create companies from scratch and remain actively involved throughout their lifecycle. Studios generate ideas internally, provide full-time operational support, and take larger equity stakes reflecting their co-founder role.
How long does it take for a venture studio startup to reach Series A?
Venture studio startups reach Series A funding in an average of 25.2 months, compared to 56 months for traditional startups. This accelerated timeline results from the studio's systematic approach, shared resources, and ability to avoid common early-stage mistakes.
Are venture studio startups more successful than traditional startups?
Yes, data shows venture studio startups achieve approximately 30% higher success rates. They have an 84% seed funding rate and 72% Series A rate compared to 42% for traditional startups. The average IRR for studio ventures is 53% versus 21.3% for conventional startups.
Who should consider joining or partnering with a venture studio?
Venture studios are ideal for entrepreneurs who value operational support and reduced risk over maximum equity ownership, investors seeking higher success rates and deeper portfolio engagement, first-time founders who benefit from structured guidance, and domain experts who have knowledge but lack complete founding teams or operational experience.
Conclusion
The venture studio model represents a fundamental evolution in how companies are created, combining the systematic efficiency of manufacturing with the innovation potential of startups. By integrating ideation, validation, team building, and operational support under one roof, studios have demonstrated their ability to build companies faster, more efficiently, and with higher success rates than traditional approaches.
For entrepreneurs willing to trade equity for comprehensive support and dramatically reduced risk, venture studios offer a compelling alternative to the traditional startup journey. For investors, the model provides access to systematically de-risked ventures with professional management from day one.
As the startup ecosystem continues to evolve, venture studios are establishing themselves as a permanent and growing segment, bridging the gap between pure capital providers and company operators. Whether you're an entrepreneur considering your next venture, an investor exploring alternative models, or a corporation seeking innovation, understanding the venture studio model is increasingly essential for navigating the modern startup landscape.